Latin: Stenella coeruleoalba
Gaelic: Leumadair-mara stiallach
CETACEAN FACTFILE:
Months: July – September
Length: Up to 2.6 metres
Range: Tropical and temperate waters
Threats: Entanglement in fishing gear, pollution
Diet: Variety of fish, squid and crustaceans
PHYSICAL DESCRIPTION
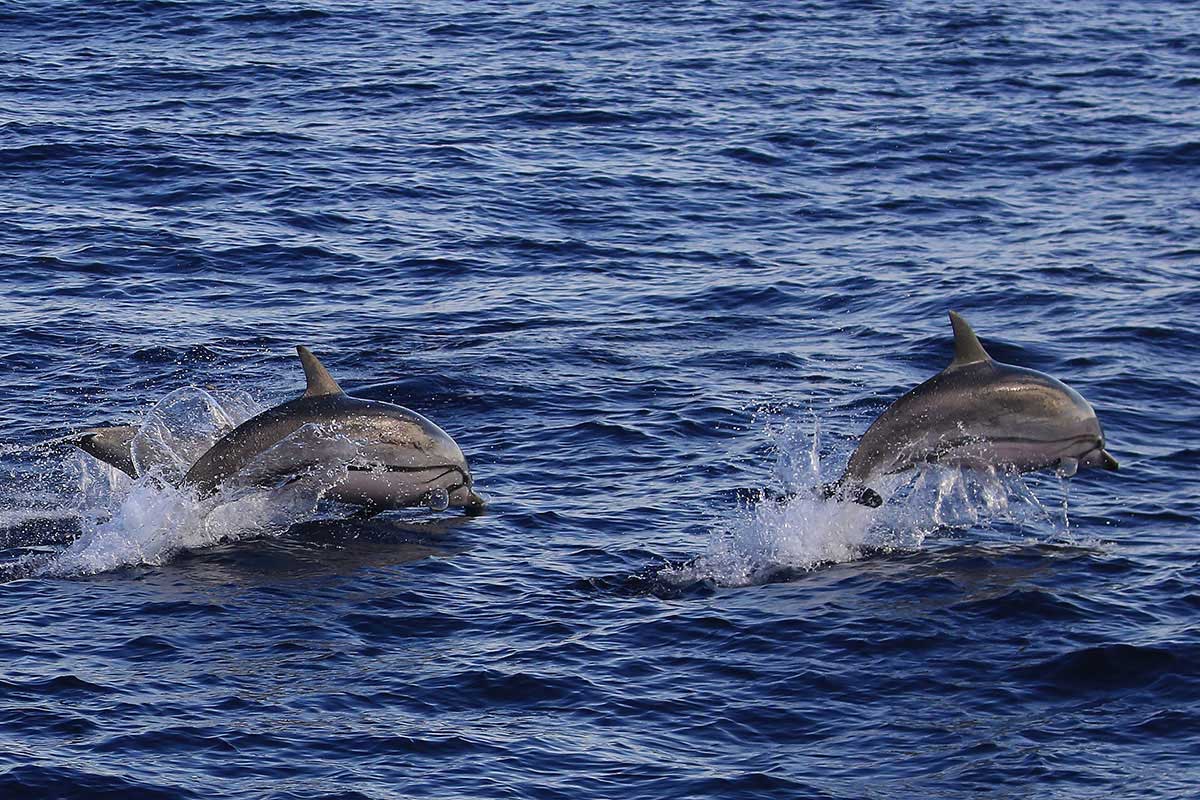
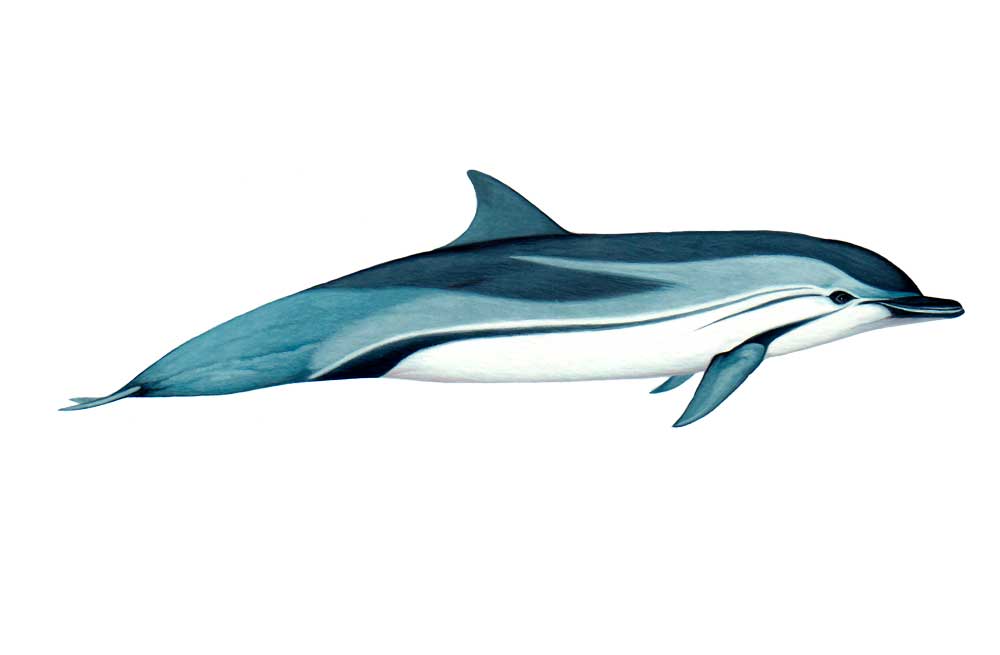
Striped dolphins are streamlined oceanic dolphins, similar in shape and size to common dolphins and measuring up to 2.6 metres in length. They have a long beak, a large curved dorsal fin and short tapered pectoral fins. Striped dolphins have a distinct colour pattern: the beak, melon, back, dorsal and pectoral fins are dark grey whilst the throat and underside are very pale; there are usually three dark grey stripes running from the eye to the anus, one to the pectoral fin and a third short stripe between the other two; the eyes are normally outlined by a dark patch; starting above the eye and a blaze of pale grey sweeps along each flank.
BEHAVIOUR
Striped dolphins can be very acrobatic, making them fairly conspicuous at the sea surface. Group size varies but they are renowned for travelling in large groups of several hundred animals, although this has not been recorded in the Hebrides. Capable of reaching speeds of up to 23 mph, striped dolphins frequently bow-ride.
HABITAT AND DISTRIBUTION
The striped dolphin is wide ranging throughout tropical and temperate waters. Although rare, sightings in UK coastal waters normally occur during the warmer summer months. Off the west coast of Scotland live sightings are rare and records include stranded animals.
FOOD AND FORAGING
The diet of the striped dolphin is varied and may include fish, squid, octopus, krill and crustaceans. They feed anywhere within the water column where prey is concentrated and they can dive to depths of 700 metres to hunt deeper-dwelling species.
STATUS AND CONSERVATION
Globally, striped dolphins are considered common within their range but they are rarely seen in UK waters. The most notable threats to striped dolphins include entanglement in fishing nets, reduction in prey availability due to overfishing and contamination from pollutants. In Japan striped dolphins are the subject of intensive drive hunts, where large groups of dolphins are driven towards the shore and killed for their meat